HighLevel’s Custom Webhook workflow action lets you send real‑time data to external services using GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE requests. Configure auth, headers, query parameters, and JSON/form payloads to connect CRMs, apps, and custom APIs—without code. This article explains setup, best practices, and working examples to help you ship reliable integrations fast.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- What is Custom Webhook?
- Key Benefits of Custom Webhook
- Authentication Options
- HTTP Methods & Request Components
- Event vs Method (UI Behavior)
- Headers & Query Parameters
- Payload & Field Mapping
- Testing & Troubleshooting
- How To Set Up Custom Webhook
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Custom Webhook?
Custom Webhook is an outbound workflow action that makes an HTTP request to a URL you choose. When a workflow run reaches this step, HighLevel assembles your headers, parameters, and payload (including mapped dynamic values) and sends the request to the external system.
Key Benefits of Custom Webhook
Understanding where Custom Webhook shines helps you pick the right automation tool and structure requests correctly for your provider.
- Flexible methods: Use GET, POST, PUT, DELETE to match any API operation.
- Authentication options: Bearer token, API key, Basic Auth, OAuth2, or No auth with custom headers.
- Precise data mapping: Dynamic values (e.g., {{contact.email}}) populate headers, params, or body so every call includes the right record details.
- Reusable patterns: Build once, reuse across workflows with consistent headers, content types, and payload shapes.
- Faster troubleshooting: Optional response capture and workflow execution logs streamline testing and issue resolution.
Authentication Options
External APIs often require credentials. Choose the option your provider supports and place secrets in headers—not URLs—for better security.
Bearer Token
Use header Authorization: Bearer <token>.
Example header:
Authorization: Bearer {{location.api_token}}API Key
Most services expect a custom header (e.g., X-API-Key: <key>). Only use query‑string keys if the provider requires it.
Header example:
X-API-Key: {{location.external_api_key}}Query example (only if required): ?api_key={{location.external_api_key}}
Basic Auth
Provide Username and Password in the action’s Authorization fields. HighLevel sends the proper Authorization: Basic ... header.
OAuth2
If your provider uses OAuth2, first configure the token in Global Workflow Settings → OAuth2 / Manage Tokens, then select it in the action. OAuth2 is recommended for providers that rotate or refresh tokens automatically.
No Auth + Custom Header
If your provider asks for a bespoke header (e.g., X-Signature: <secret>), choose No auth, then add the header under Headers.
HTTP Methods & Request Components
Matching the correct method and placing data in the right part of the request prevents 400/401/422 errors and speeds up integrations.
- URL & Path Parameters: You can include variables in the path, e.g., https://api.example.com/contacts/{{contact.id}}.
- GET: Retrieve data. Bodies are typically ignored—use query parameters: https://api.example.com/leads?email={{contact.email}}&status=active
- POST: Create resources. Send a JSON body or form data (see Content‑Type).
- PUT: Update resources. Usually requires an ID in the path and a JSON body.
- DELETE: Remove resources. Often includes the ID in the path.
- Content‑Type: Common values: application/json (JSON body) or application/x-www-form-urlencoded (form fields). Match your provider’s docs.
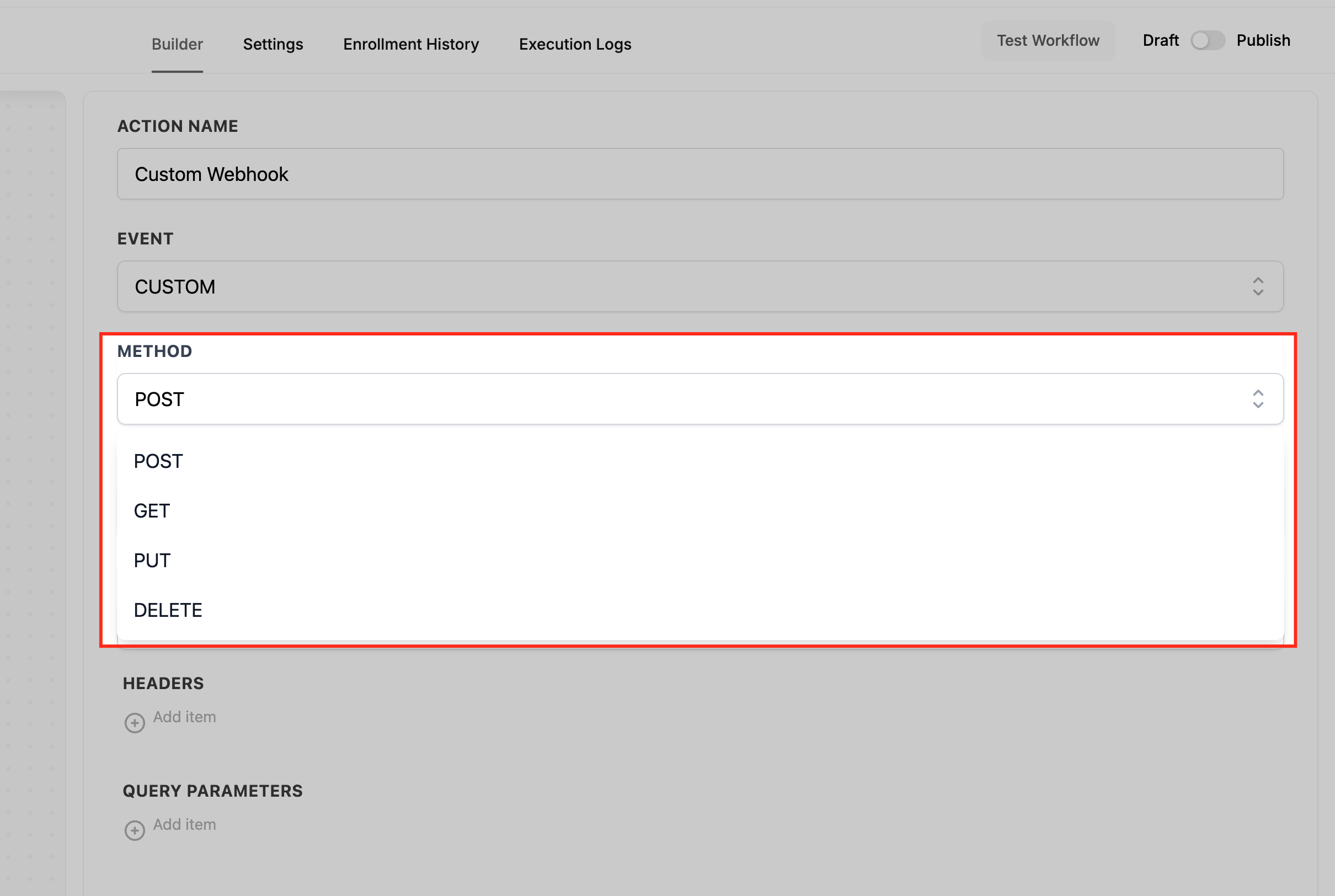
Event vs Method (UI Behavior)
The Custom Webhook action offers two configuration modes. CUSTOM exposes full control (method, content type, raw body). GET/POST offer simplified experiences. Pick the mode that matches your provider’s requirements.
Event = CUSTOM (advanced):
Shows Method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE), Content-Type, and Raw Body editor for JSON or other formats.
Best when you need JSON payloads, non‑POST methods, or explicit headers/content types.
Event = POST (simple):
Shows Body (Key and Value) pairs for a form‑style payload; no Raw Body editor.
Use for simple key/value submissions. Switch to CUSTOM if your provider expects JSON.
Event = GET (simple):
No request body. Use Query Parameters for filters. Save response from this Webhook is available.
Event picker:
The Event dropdown controls which fields appear. Choose CUSTOM for full control.
Variable picker:
The small tag icon next to fields (URL, Headers, Query Params, Body) opens the dynamic value picker to insert values like {{contact.id}}.
Headers & Query Parameters
APIs commonly require specific headers and query parameters for auth, content type, versioning, or filtering. Map dynamic values when needed.
Headers (examples):
Authorization: Bearer {{location.api_token}} Content-Type: application/json X-API-Key: {{location.external_api_key}} X-App-Version: 2024-11-01Query parameters (examples):
lead_id={{contact.id}} email={{contact.email}} source=workflowAvoid putting secrets in query strings unless your provider requires it.
Payload & Field Mapping
Dynamic values let you personalize each request with contact, opportunity, or other workflow data—shaped to match the external API.
Flat JSON payload (POST / create):
{ "id": "{{contact.id}}", "first_name": "{{contact.first_name}}", "last_name": "{{contact.last_name}}", "email": "{{contact.email}}", "phone": "{{contact.phone}}" }Nested JSON:
{ "contact": { "id": "{{contact.id}}", "name": "{{contact.name}}", "phones": ["{{contact.phone}}"], "tags": ["{{contact.tag}}", "new-lead"] } }Form‑encoded: Set Content‑Type to application/x-www-form-urlencoded and provide key/value pairs instead of JSON.
Testing & Troubleshooting
Validating requests before you go live prevents broken automations. Use both provider‑side tools and workflow logs.
- Use Test Workflow (draft mode) with a sample record to trigger the action.
- Send test calls to tools like Webhook.site or Postman collections to confirm headers, params, and payload shape.
- Verify basics first: correct URL, method, Content‑Type, required headers, and valid credentials.
- Check Execution Logs / run history to confirm the action fired and review status codes.
- If you don’t see Content‑Type or a Raw Body editor, verify the Event selection. Choose CUSTOM for JSON payloads or PUT/DELETE requests.
Common HTTP responses:
400/422 Invalid payload → match the provider’s required fields and types.
401/403 Unauthorized/Forbidden → fix token, key, scope, or account permissions.
404 Wrong path/ID → confirm endpoint and path variables.
409 Conflict/idempotency → ensure unique IDs or follow provider’s upsert rules.
429 Rate limited → slow down or add delays/retries per provider limits.
5xx Provider error → retry later and contact provider support.
How To Set Up Custom Webhook
A clear, repeatable setup reduces errors and ensures your requests match the provider’s expectations. Use the steps below to configure the URL, event/method, authorization, headers/params, and payload correctly before testing.
Open your workflow
Navigate to Automation → Workflows and open the workflow where you want to send data so the run reaches this action with the right record context.

Add the action
Click + Add action → Send Data → Custom Webhook to create the step that will make the outbound HTTP call. Screenshot (placeholder): Action Drawer — Add the Custom Webhook action from Send Data. Alt text: Workflow action drawer showing Webhook and Custom Webhook.

Name the action
Give the action a clear, descriptive name to simplify reading and troubleshooting later; for example, Send Lead to External CRM.

Select the Event (and Method when applicable)
Choose the Event that matches your use case. CUSTOM reveals the Method picker (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE), Content-Type, and a Raw Body editor for JSON or other formats. POST provides a simple Body (Key and Value) interface without a raw body editor. GET has no body; use Query Parameters to pass filters. The small tag icon next to fields opens the dynamic value picker (for example, {{contact.id}}).

Enter the URL
Paste your provider’s endpoint and include variables in the path when needed, such as https://api.example.com/leads/{{contact.id}}, so each request targets the correct record.

Choose Authorization
Select the authentication method required by the provider—Bearer Token, API Key, Basic Auth, OAuth2, or None (with custom headers)—and supply credentials exactly as specified to avoid 401/403 errors.

Add Headers and Query Parameters (if needed)
Provide required headers like Content-Type, Authorization, and any custom keys, and add query parameters for GET filters or URL-based options; dynamic values such as email={{contact.email}} ensure each call is personalized.


Save response from this Webhook (optional)
Enable response capture if it is available in your account to aid troubleshooting and record-keeping.
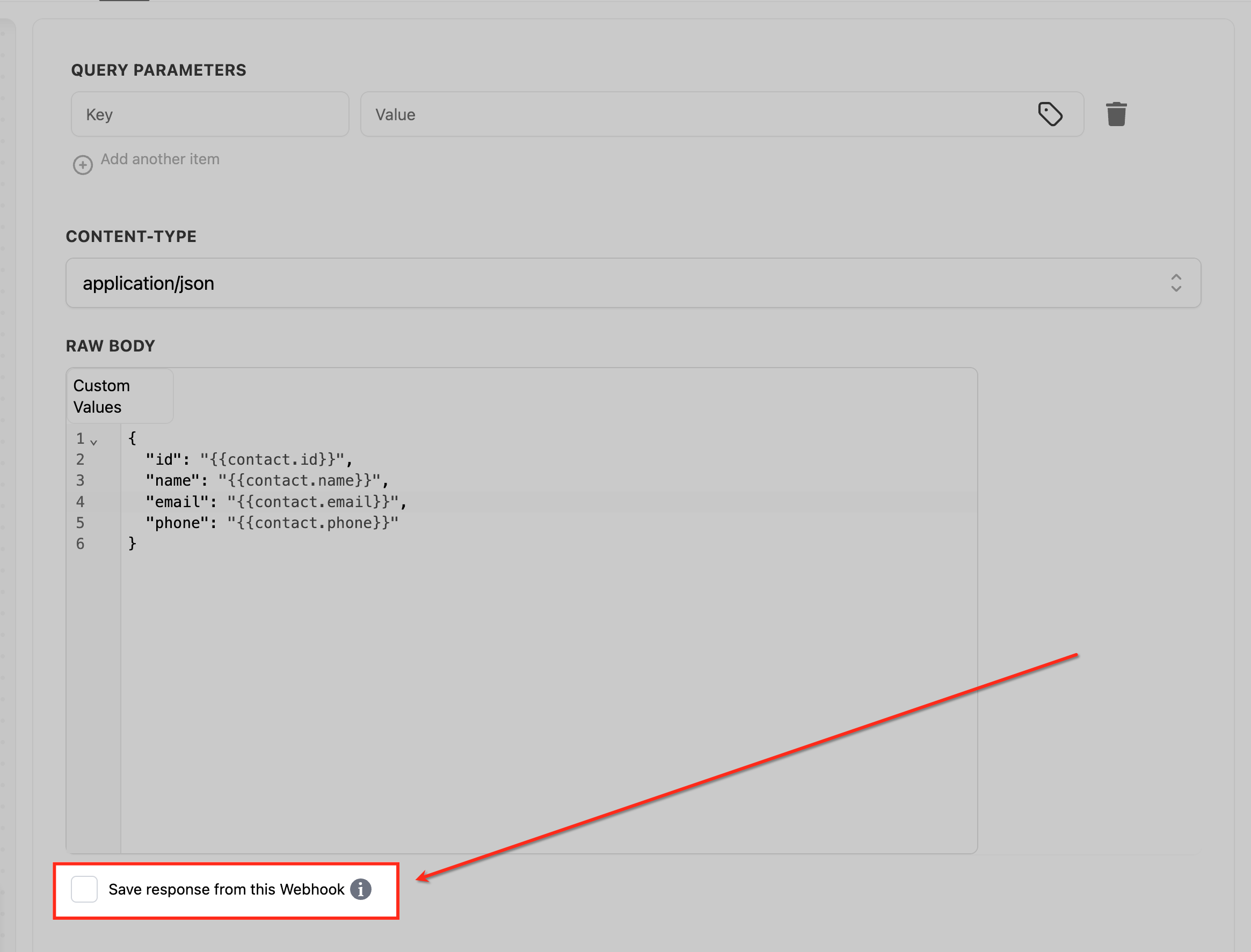
Save and test
Click Save Action, trigger a test with a sample record or a sandbox endpoint such as Webhook.site or Postman, and review Execution Logs alongside provider logs to confirm status codes and payload shape before going live.
Additional screenshot placeholders (add later if available):
OAuth2 token management: Global Workflow Settings → OAuth2 / Manage Tokens (token redacted).
Execution Logs showing a successful 200 response.
Postman/Webhook.site confirming receipt of the payload.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Do I need a specific workflow trigger for Custom Webhook to work?
No. Any workflow trigger can be used. Ensure your mapped variables (e.g., contact fields) exist at runtime.
Q: My provider requires a static IP allowlist. Can HighLevel provide one?
No. Use header‑based authentication (Bearer/API Key/Basic/OAuth2) instead and share the required credentials with your provider.
Q: Where do I put my API key header or query string?
Prefer a header (e.g., X-API-Key). Only use query‑string keys if the provider specifically requires it.
Q: Why am I getting 401/403 errors?
Invalid or missing credentials, wrong auth type, expired token, or insufficient scopes/permissions. Re‑check Authorization and required headers.
Q: The provider says my JSON is invalid (400/422). What should I check?
Confirm Content‑Type, required fields, data types, and nested structure. Compare to the provider’s schema or run a Postman test.
Q: Can I include arrays or nested objects in the payload?
Yes. Build nested JSON or arrays and map dynamic values where needed (see examples above).
Q: Can I capture and review the response?
If available in your account, enable Save response from this Webhook and review the workflow’s Execution Logs and provider logs.
Q: How do I decide between Custom Webhook and Webhook (Outbound)?
Use Custom Webhook when you need advanced auth and flexible request building. Use Webhook (Outbound) for simpler, pre‑defined patterns.
Was this article helpful?
That’s Great!
Thank you for your feedback
Sorry! We couldn't be helpful
Thank you for your feedback
Feedback sent
We appreciate your effort and will try to fix the article